Biology
Biology related concepts
curated by Benetech
Resources 59
-

Covers these important topics: external anatomy, physical and emotional changes of puberty, health and hygiene, and privacy and safety.
(Source: DCMP)
-

Intended for older male students with special needs. Covers these important topics: external anatomy, physical and emotional changes of puberty, health and hygiene, privacy, and safety.
(Source: DCMP)
-

Covers these important topics: external anatomy, physical and emotional changes of puberty, health and hygiene, and privacy and safety in female.
(Source: DCMP)
-

Intended for older female students with special needs. Covers these important topics: external anatomy, physical and emotional changes of puberty, health and hygiene, privacy, and safety.
(Source: DCMP)
-
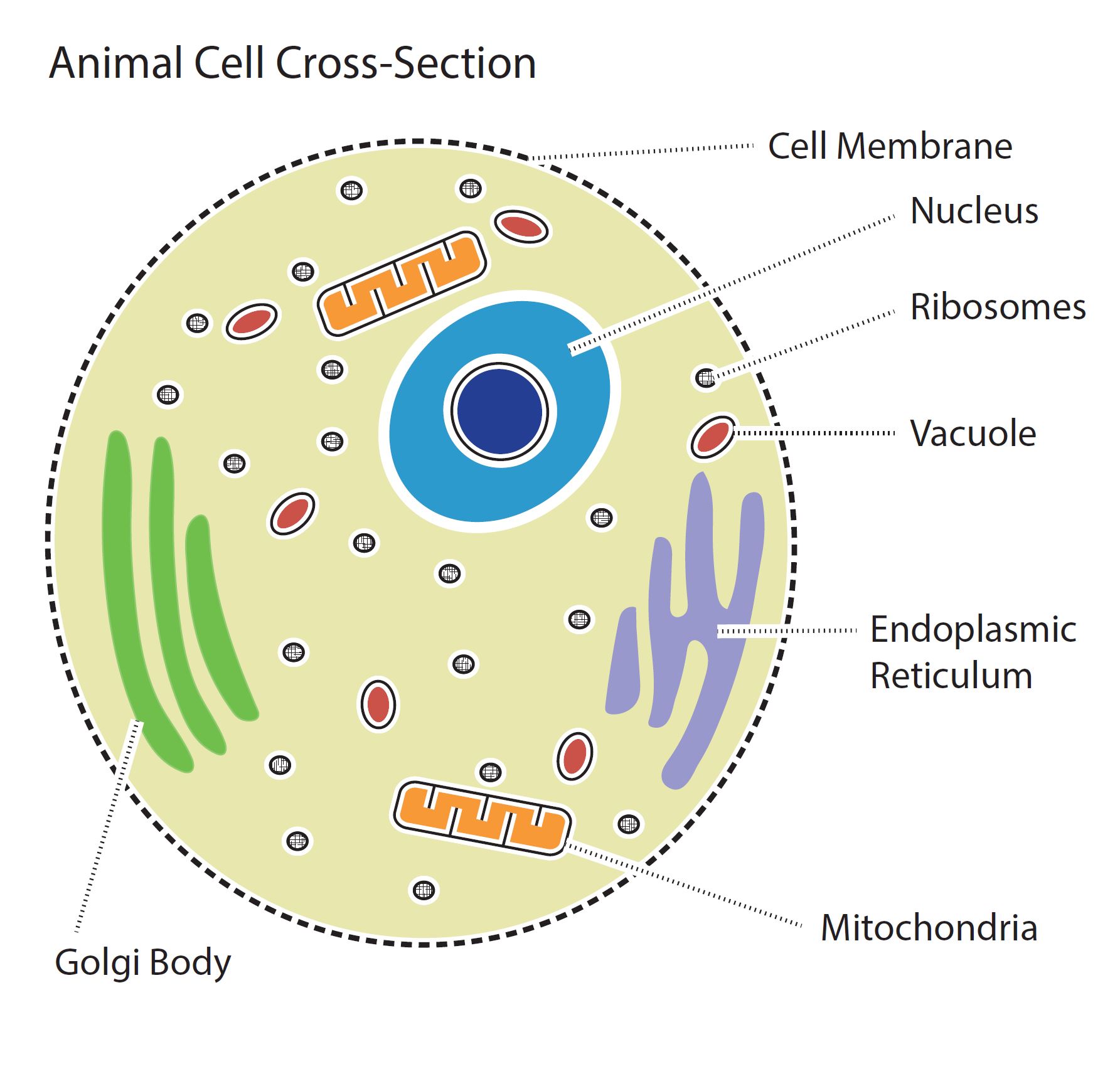
Animal Cell
-
 Image
Image
-
 Text Document
Text Document
-
 PDF
PDF
-
 2.5D Tactile Graphic
2.5D Tactile Graphic
Basic educational diagram showing a cross section of an animal cell. Design modalities for the image include braille with and without labels, print with and without labels in greyscale, color, and texture.
(Source: Benetech)
-
-
Bacterial colonies
-
 Image
Image
-
 3D Model
3D Model
-
 PDF
PDF
-
 Audio File
Audio File
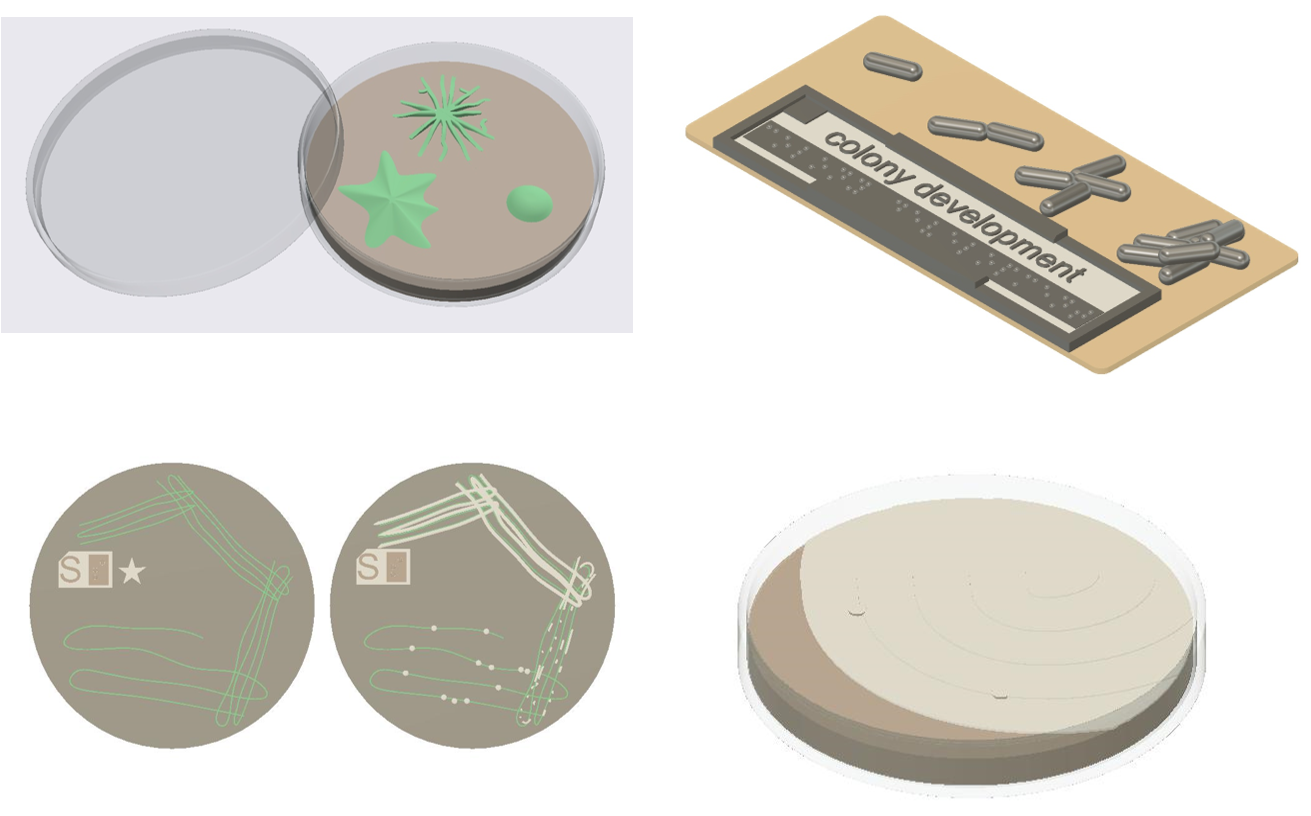

Colony formation on semi-solid medium is basic characteristic of many different bacteria and an important property for microbiologists. These models illustrate the different types of colonies formed, what a colony reflects at the cellular level, how microbiologists obtain isolated colonies, and what happens when cells swarm instead of forming colonies.
(Source: MicroBVI)
-
-
Bacterial cell shapes and organization
-
 Image
Image
-
 3D Model
3D Model
-
 PDF
PDF
-
 Audio File
Audio File
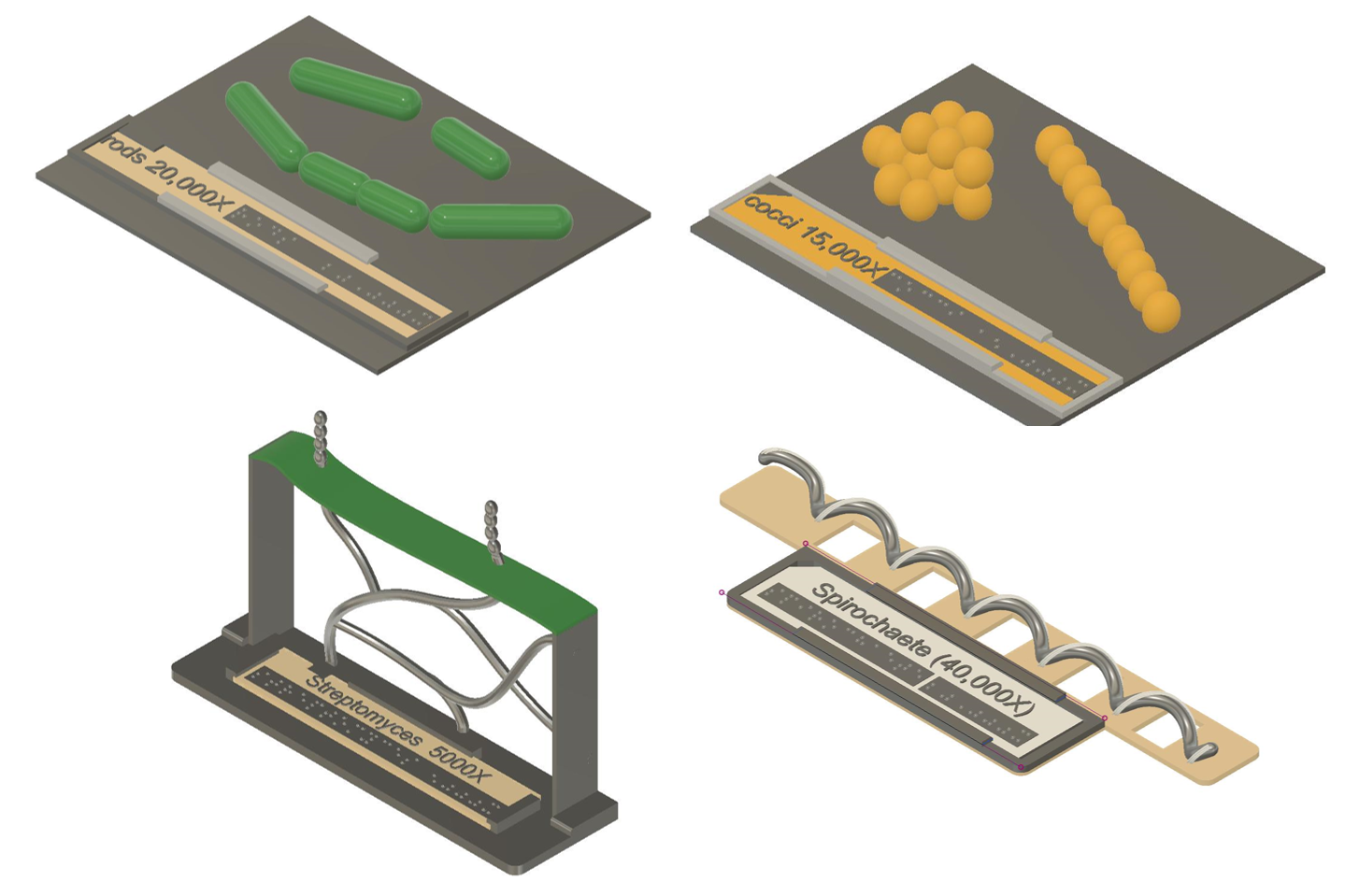
The most common bacterial shapes are rods, cocci (round), spirals and filaments. Groups of these cells can be differently arranged in space. Four 3D-printable models illustrate these shapes and arrangements.
(Source: MicroBVI)
-
-
Bacterial cell cycle and exponential growth
-
 Image
Image
-
 3D Model
3D Model
-
 PDF
PDF
-
 Audio File
Audio File
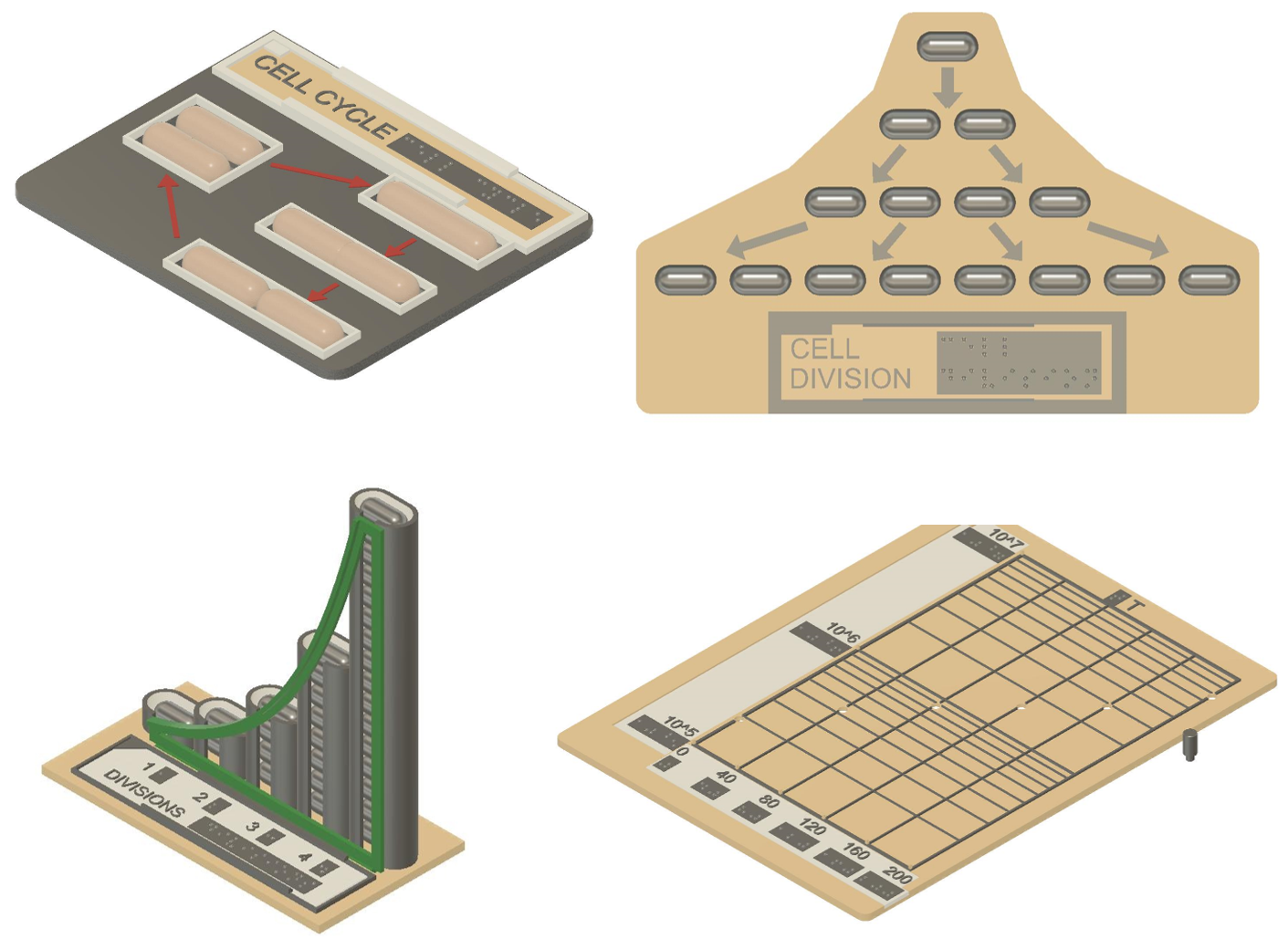
Most bacteria grown by fission, one cell dividing into two. When nutrients are abundant, this can result in exponential growth, with a large increase in the number of cells over a surprisingly short period of time. Bacterial cell division and the characteristics of exponential growth are illustrated with four, 3D printable models
(Source: MicroBVI)
-
-
Beyond Genetics
-
 Video
Video

Nature vs. Nurture is a long-running debate in the social sciences. While human genetics is an important part of the story, recent scientific developments suggest that the way genes actually work can be critically shaped by the environment in which one lives. Dr. Nessa Carey and Dr. Guy Sutton explore the ways epigenetics gives a new and exciting dimension to the debate.
(Source: DCMP)
-
-

Biodiversity, or biological diversity, refers to the variety of plants, animals, and microorganisms that exist. The biodiversity of an environment is important because it helps keep the environment in a natural balance. An ecosystem which is species-rich is more resilient and adaptable to external stress than one in which the range of species is limited. Part of the "Biology" series.
(Source: DCMP)
-

Biology is the study of life. It encompasses the cellular basis of living things, the energy that underlies the activities of life, and the genetic basis for inheritance in organisms. Topics covered include the smallest components of living things: atoms, molecules, organelles, and cells. Part of the "Biology" series.
(Source: DCMP)
-
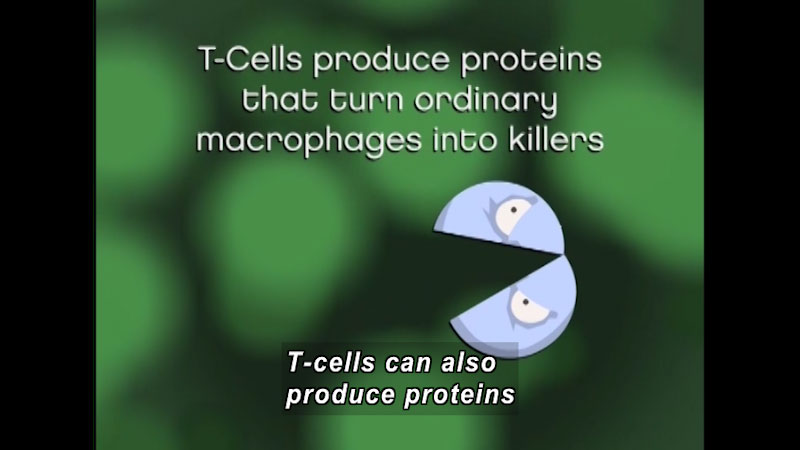
Homeostasis refers to the body’s ability to maintain a stable internal environment, and maintaining homeostasis requires that the body continuously monitors its internal conditions. From body temperature to blood pressure to levels of certain nutrients, each physiological condition has a particular set point. Topics covered include homeostasis, negative feedback loop, nervous system, endocrine system, digestive system, excretory system, musculoskeletal system, and the immune system. Part of the "Biology" series.
(Source: DCMP)
-
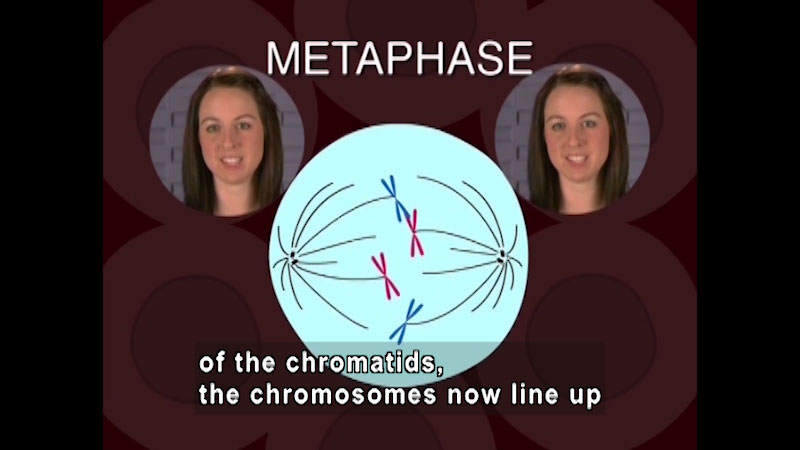
The cell cycle is the series of events that cells go through as they grow and divide. This title provides a discussion on each of the stages of the cell cycle: prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase, and cytokinesis. Part of the "Biology" series.
(Source: DCMP)
-

In the early 1950s, American biologist James Watson and British physicist Francis Crick came up with their famous model of the DNA double helix. The structure of DNA, as represented in Watson and Crick's model, is a double-stranded helix. The sugar-phosphate backbones of the DNA strands make up the outside of the helix, while the nitrogenous bases are found on the inside and form hydrogen-bonded pairs that hold the DNA strands together. Other topics covered include DNA replication, RNA transcription, and RNA translation. Part of the "Biology" series.
(Source: DCMP)
-

From fossil evidence, it appears that life may have existed on Earth as early as 3.5 billion years ago. This suggests that life must have evolved sometime during Earth's tumultuous first billion years. How did life evolve? What did early forms of life look like? Topics covered include protocells, endosymbiosis, prokaryotes, eukaryotes, evolution, heredity, variation, natural selection, genetic drift, and gene flow. Part of the "Biology" series.
(Source: DCMP)
-
Brain
-
 Image
Image
-
 Text Document
Text Document
-
 PDF
PDF
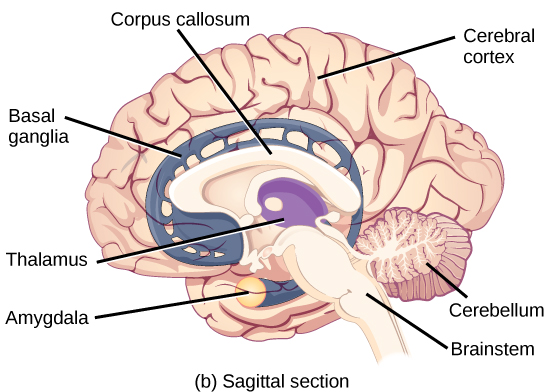
Sagittal, or side view of the human brain shows the different lobes of the cerebral cortex. The frontal lobe is at the front center of the brain. The parietal lobe is at the top back part of the brain. The occipital lobe is at the back of the brain, and the temporal lobe is at the bottom center of the brain. The motor cortex is the back of the frontal lobe, and the olfactory bulb is the bottom part. The somatosensory cortex is the front part of the parietal lobe. The brainstem is beneath the temporal lobe, and the cerebellum is beneath the occipital lobe.
(Source: OpenStax)
-
-
Calvin Cycle
-
 Image
Image
-
 Text Document
Text Document
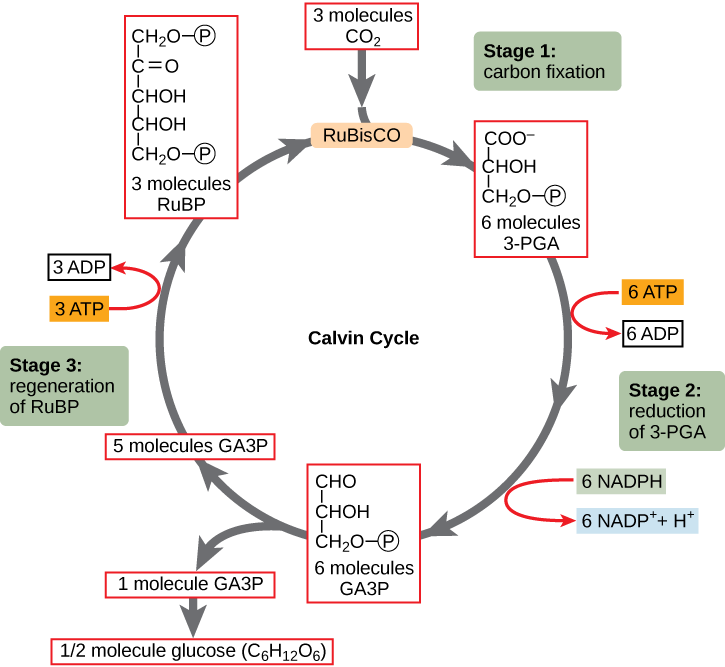
Calvin cycle showing how carbon dioxide and other compounds are converted into glucose.
(Source: OpenStax)
-
-
Carbon Cycle
-
 Image
Image
-
 Text Document
Text Document
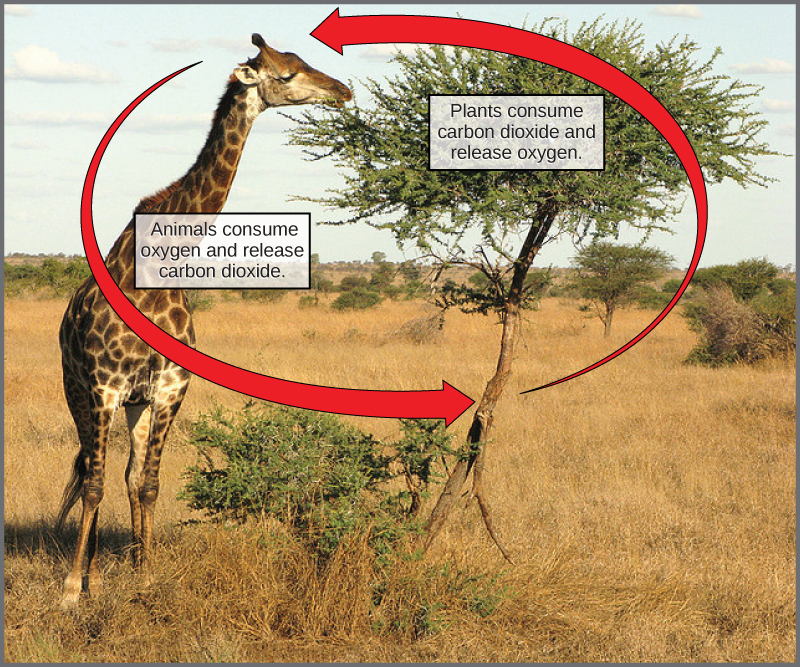
Illustration showing the carbon cycle using animals and plants.
(Source: OpenStax)
-
-
Cell Processes
-
 Video
Video

Discusses how the activities and processes of cells affect our lives. Covers metabolism, diffusion, respiration, and cell growth and mitosis. Includes questions and a quiz.
(Source: DCMP)
-
-
Cells (Spanish)
-
 Video
Video
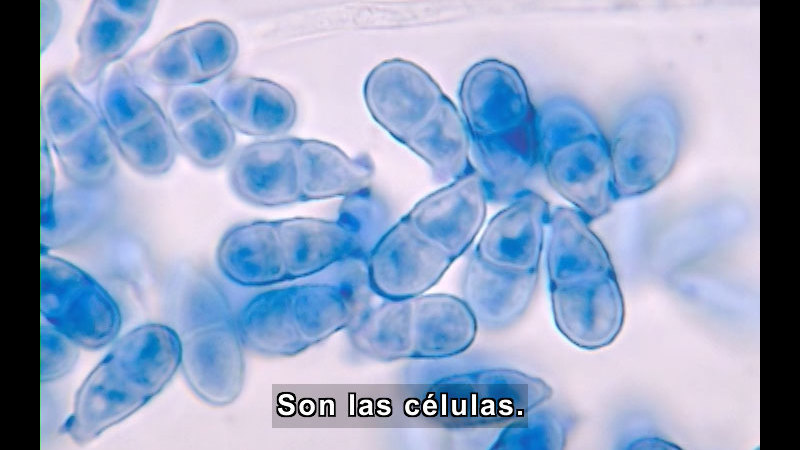
Students explore the smallest, but most important units of life: cells. They also gain an understanding of common cell parts through lifelike animations. Additional concepts and terminology include building blocks of life, animal cell, cell membrane, nucleus, cytoplasm, plant cell, photosynthesis, cell wall, chloroplasts, organelles, and role of cells in the body.
(Source: DCMP)
-
-
Cells And Molecules
-
 Video
Video
Part of the "Visualizing Cell Processes" series. Includes the following modules: "The Cell Machinery," "A Variety of Cells," "Organic Molecules: The Building Blocks of Life," "Prokaryote Evolution and Diversity," and "Independently Living Eukaryotic Cells."
(Source: DCMP)
-
-
Cells And Tissues
-
 Video
Video
Uses microphotography and graphics to examine different kinds of plant and animal cells, discussing their structures and tissues. Defines mitosis and meiosis as forms of cell division and illustrates each. Video has three 5-minute segments for convenience.
(Source: DCMP)
-
-
Cells Video Quiz
-
 Video
Video
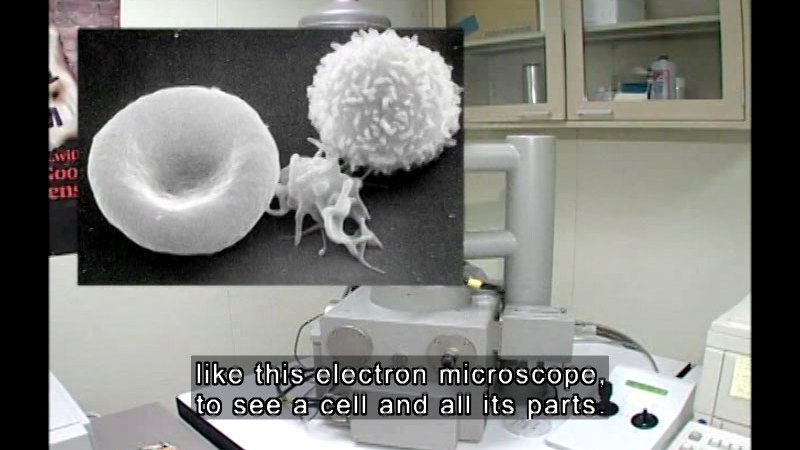
Introduces cells, how they function, the differences between plant and animal cells, and the various parts of the cell. A quiz is given after each topic.
(Source: DCMP)
-
-
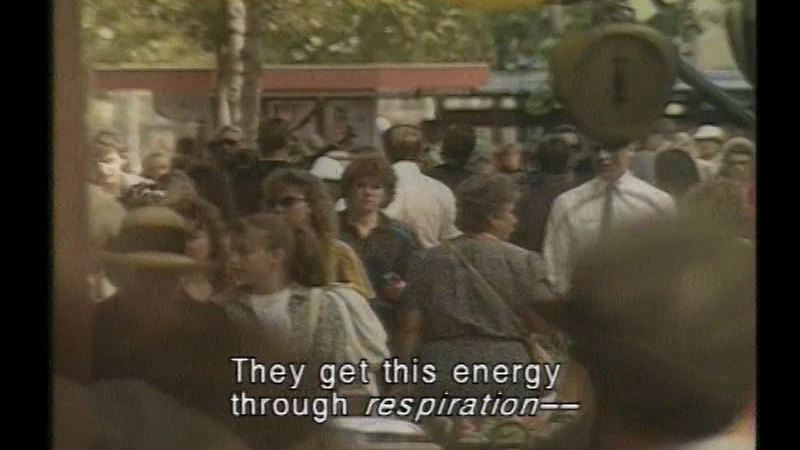
Explains the scientific concepts of photosynthesis, respiration, and enzymes. Laboratory experiments demonstrate: the rate of photosynthesis in greenhouse plants; the amount of oxygen used by the body during respiration at varying speeds; and the reaction times of different enzymes.
(Source: DCMP)
-
Classification Systems
-
 Video
Video

Research in biology would be impossible without a common framework for grouping and distinguishing species. Carl Linnaeus was the first to propose a classification system of organisms. His system developed into the organizational structure used in the life sciences today. Viewers also learn how new scientific names are created and how the existing system has been further refined using DNA studies.
(Source: DCMP)
-
-
Cycles In Living Things
-
 Video
Video

Crisp, vivid video footage illustrates how living things change throughout their lives. Focuses on the life cycles of plants, insects, and frogs.
(Source: DCMP)
-
-
Covid-19 Model
-
 Image
Image
-
 Video
Video
-
 3D Model
3D Model
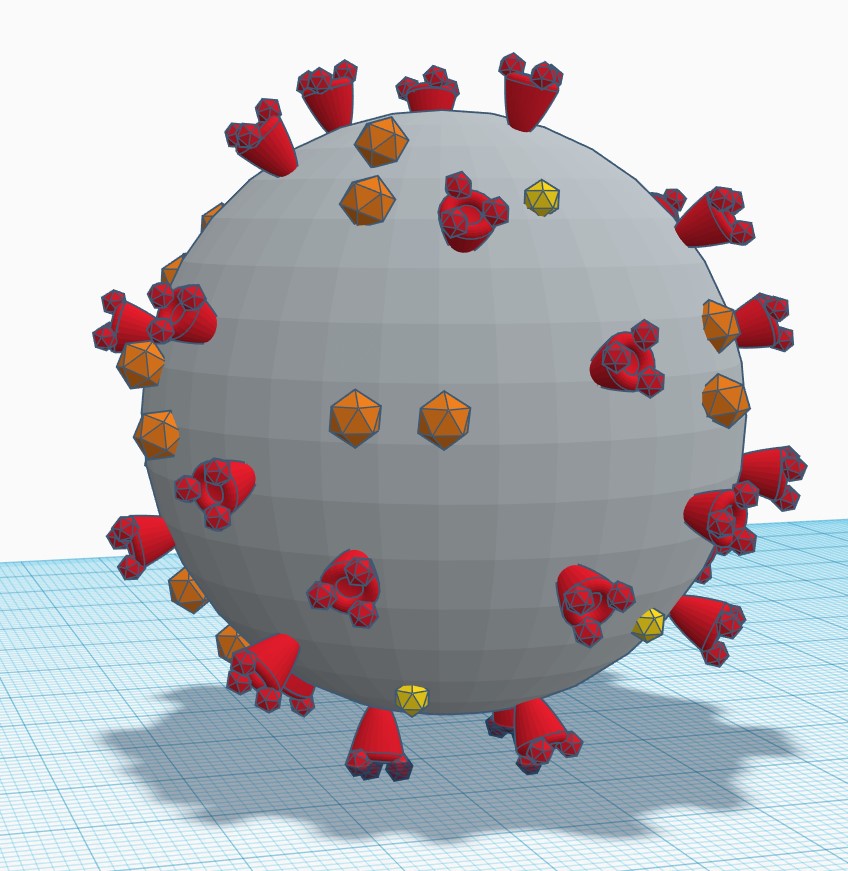
Covid-19 image, 3D model with accompanying video exploration of the 3D model.
(Source: North Carolina Central University)
-
-
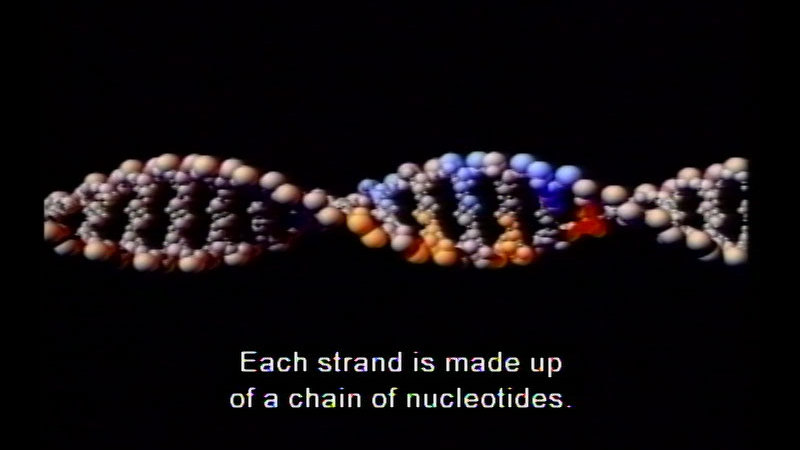
Part of the "Visualizing Cell Processes" series. Includes the following modules: "Mitosis: Chromosome Condensation," "Mitosis: Stages," "Cytokinesis," "Meiosis," "Nucleotide Structure and Bonding," "Replication Enzymes," "Replicating the Strands," "The Twisting Problem," and "Proofreading and Repair."
(Source: DCMP)
-
Danger Virus
-
 Video
Video

Draws on documentary and archival footage, 3-D and 2-D animations, and high-tech imaging to investigate a variety of virological topics: the nature of pandemics as illustrated by the SARS outbreak in China; genetic sequencing of Spanish influenza from exhumed tissue of a century-old corpse; how animal viruses jump the species barrier; the dissection of live viruses in a biosafety level-4 lab; the work of an Ebola research team in Gabon; the discovery of mimivirus; applications of Onyx-015, a genetically engineered adenovirus; and more. Features Vincent A. Fischetti of The Rockefeller University, Jeffery Taubenberger of the Armed Forces Institute of Pathology, Y. Guan of The University of Hong Kong, Didier Raoult of the French National Center for Scientific Research, and other leading virus specialists.
(Source: DCMP)
-
-
Exploring Bacteria
-
 Video
Video
Where do bacteria live, and how long have they been here? How can you tell them apart? What do they do to people and the environment? Answers these and other questions in this overview. Examines the fundamental structure of the bacteria cell, types of bacteria, and their importance to humans and the environment.
(Source: DCMP)
-
-
Genes And Cloning
-
 Video
Video
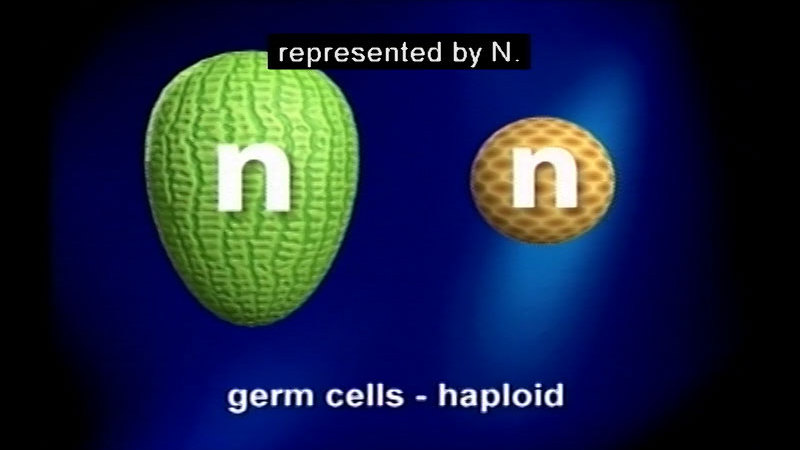
Genetic modification of organisms and cloning is controversial. Looks at the way humanity has modified genomes of plants and animals used for food since the dawn of agriculture. As knowledge of cells and genetics has increased, so has humanity's ability to alter genomes. Shows animations of how genetic engineers are now able to construct and insert genes for desirable characteristics into plants and how technology is used to increase numbers of animals with desirable traits and screen out those with disease or lower food yields.
(Source: DCMP)
-
-
Genes As Medicine
-
 Video
Video

Gene therapy is a method for treating inherited diseases by delivering corrective versions of genes to patients. Dr. Jean Bennett and Dr. Albert Maguire focused their careers on developing a successful gene therapy for an inherited form of childhood blindness called Leber congenital amaurosis (LCA). This documentary tells the story of how the LCA gene therapy was developed. Students will learn how autosomal recessive conditions are inherited, how scientists can use modified viruses to deliver human genes to cells, what makes the eye an ideal tissue for gene therapy, and how model organisms are used to test treatments before they are tested in patients.
(Source: DCMP)
-
-
Genes, Genetics & DNA
-
 Video
Video

Genes, those traits passed down to us by our parents, are the things that make each of us different from the others. This question-answer format covers basic information about genes, chromosomes, cell division, dominant and recessive genes, and fertilization. Illustrates Mendel's rules of heredity. Covers advances in the fields of DNA, genetic engineering, and gene therapy. Reviews major points.
(Source: DCMP)
-
-

No organism lives forever. The length of time animals and humans live is influenced by their genes. Scientists have made astonishing discoveries concerning the role of genetics in determining life span, and this holds promise of extending the lives of animals and humans. Explains genetics, DNA, and genetic theories of aging. Illustrates the genetic processes behind cellular aging, and shows how genes affect life span. Discover the reasons why cells age and why a certain enzyme can effectively turn back the hands of our "biological clock."
(Source: DCMP)
-
Homeostasis
-
 Video
Video
Presents three key biological concepts about homeostasis: controlling body temperature, controlling water level, and controlling blood sugar. Each concept is illustrated with a variety of experiments and computer animation to illuminate what is happening both visibly and at the molecular level.
(Source: DCMP)
-
-
How Cells Are Controlled
-
 Video
Video

Part of the "Inside the Living Cell" series. Illustrates how genetic instructions carried on DNA are transcribed into RNA, leading to the production of specific enzymes that control the thousands of biochemical processes occurring in living cells. Provides an overview of the protein basis of life, enzymatic reactions, amino acids and DNA, how proteins are built, and gene activation.
(Source: DCMP)
-
-
How Cells Obtain Energy
-
 Video
Video

Part of the "Inside the Living Cell" series. Illustrates the mechanisms of photosynthesis and cellular respiration. Introduces adenosine triphosphate, or ATP, the universal energy carrier molecules that supply energy-hungry reactions. Also outlines the structure and function of chloroplasts and mitochondria, energy transforming organelles. Overviews ATP and chemical energy, mitochondria, aerobic respiration, chloroplasts, and the reactions of photosynthesis.
(Source: DCMP)
-
-
How Cells Reproduce
-
 Video
Video
Part of the "Inside the Living Cell" series. Shows how DNA replicates; how copy errors occur and are subsequently corrected by repair enzymes; and how DNA is compressed into chromosomes, making mitosis and cell division possible. Provides an overview of DNA structure, replicating DNA, mutations that change the genetic code, proofreading and repair, and the stages of mitosis.
(Source: DCMP)
-
-
Inside A Cell
-
 Video
Video

Delves into the inside of a cell. Provides the proper labeling of the important parts of the cell and the function each part performs. Discusses how cells are the basic building blocks for life and how cells can create and store energy.
(Source: DCMP)
-
-
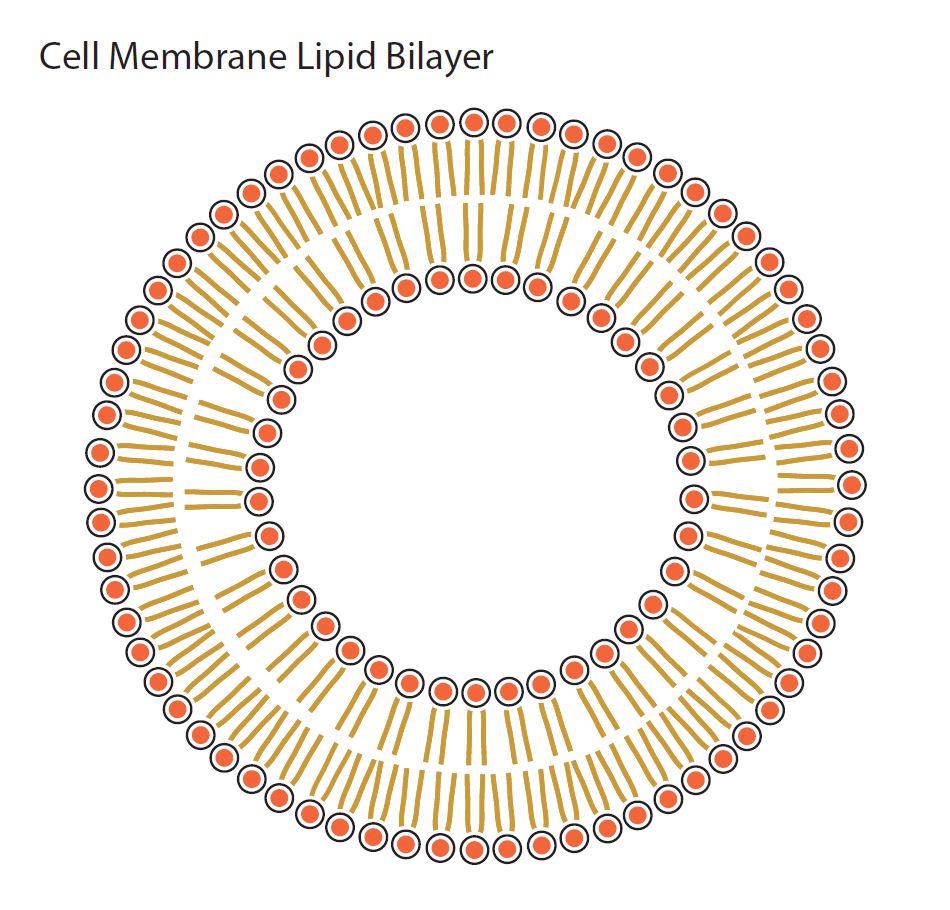
Lipid Bilayer
-
 Image
Image
-
 PDF
PDF
-
 2.5D Tactile Graphic
2.5D Tactile Graphic
-
 Text Document
Text Document
Diagram of a basic lipid bilayer. Design modalities for the image include braille with and without labels, print with and without labels in greyscale, color, and texture.
(Source: Benetech)
-
-
Massive Blood Loss
-
 Video
Video

Part of the "Gunther's ER" series. As Dr. Gunther von Hagens makes clear, a shortage of blood can mean that insufficient oxygen is reaching the major organs, usually resulting in shock and organ failure. Opens with a graphic bleeding demonstration, re-creating injury to blood vessels in the hand of a cadaver. Also examines the consequences of blood loss in the body's vital organs by creating knife wounds in the torso of a frozen body, then sawing it into slices to reveal the path of the blades and the shocking extent of the damage. Also explores a lesser well-known cause of blood loss-fractured bones-which von Hagens illustrates in an experiment in which a femur dissected from a fresh cadaver is made to bleed as it would in life. NOTE: Viewer discretion is advised. Contains clinically explicit language and nudity.
(Source: DCMP)
-
-
Me And My Body (Spanish)
-
 Video
Video

Storyteller Heather Forest uses song, pantomime, games, and discussion to introduce young students to the human body. Talks about key body parts and how they move; how the heart, lungs, and brain keep the body running; how the bones, joints, and muscles hold the body up and help it move; and how our senses help us enjoy the world. Introduces principles of healthy eating, daily exercise, and adequate rest.
(Source: DCMP)
-
-
Paramecium
-
 Video
Video
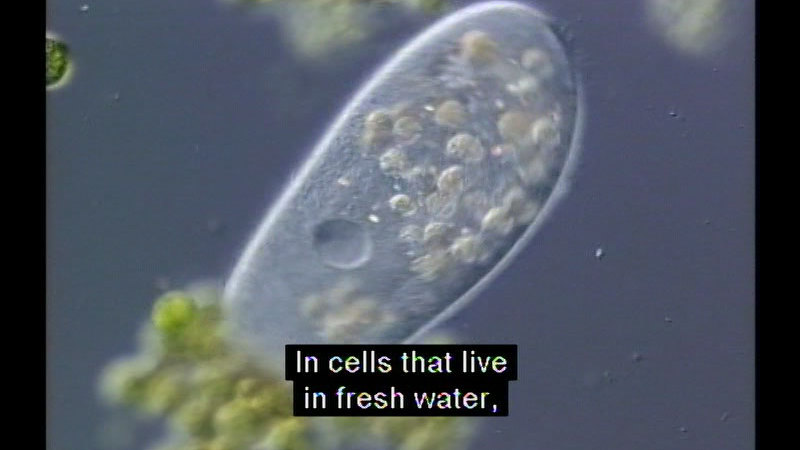
Part of the "The Biology Classics" series. Paramecia are a group of unicellular ciliate protozoa. Shows how paramecia move, feed, digest, assimilate nutrients, achieve water balance, deploy defensive weapons, reproduce, and engage in the sexual exchange of genetic material. Utilizes state-of-the-art microscopy techniques to present a compelling new picture of the life of paramecia.
(Source: DCMP)
-
-
Photosynthesis
-
 Video
Video

Photosynthesis converts light energy from the sun into chemical energy stored in organic compounds, which are used to build the cells of producers and ultimately fuel ecosystems. After providing an overview of photosynthesis, a series of animations describe the inside of the cells of a leaf to explain how the reactions of photosynthesis happen.
(Source: DCMP)
-
-
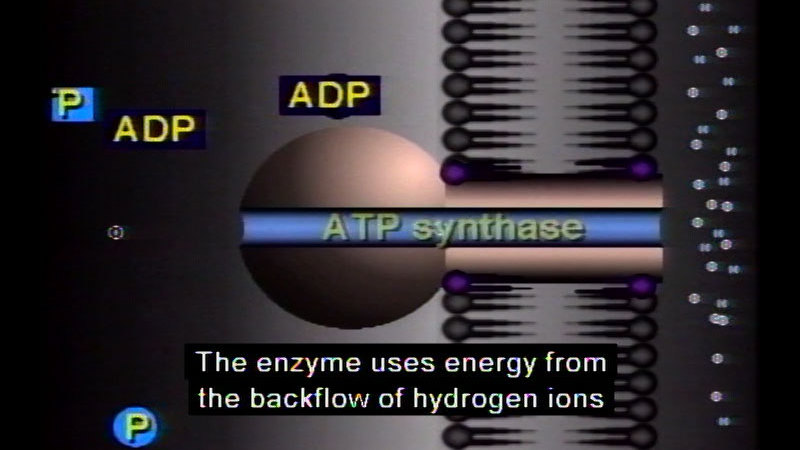
Part of the "Visualizing Cell Processes" series. Includes the following modules on photosynthesis: "Chloroplast Structure," "Light Trapping by Chlorophyll," "Light–Dependent Reactions of Photosynthesis," and "The Light–Independent Reactions of Photosynthesis." Includes the following modules on cellular respiration: "Glycolysis and Fermentation," "Mitochondrion Structure," "Aerobic Respiration," "Krebs Cycle," "Electron Transport Chain," and "ATP synthesis."
(Source: DCMP)
-

Discusses the terminology, processes, and products related to photosynthesis. Questions bridge segments and lead to information on tropism, seed structure, and germination. Includes a review and a quiz.
(Source: DCMP)
-

Biological vectors carry and transmit diseases that affect plants, animals, and humans. This program focuses on diseases transmitted by mosquitoes and ticks. Students will learn how scientists use the information they gather to help control and prevent the transmission of vector-borne diseases around the world. Part of the "Real World Science" series.
(Source: DCMP)
-
Respiration
-
 Video
Video
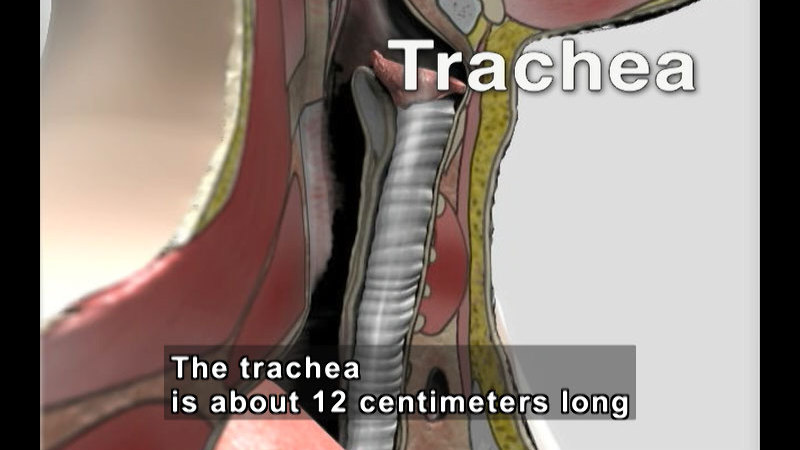
With every breath you take, the process of respiration is supplying cells in the body with oxygen they need to carry out important processes. This program highlights the major structures and functions of the respiratory system. Concepts and terminology include: nasal passage, pharynx, larynx, lungs, diaphragm, trachea, bronchial tubes, alveoli, gas exchange, pulmonary circulation, inhalation, exhalation, hemoglobin, asthma, bronchitis, smoking, lung cancer, and pneumonia.
(Source: DCMP)
-
-
Simply Cells
-
 Video
Video
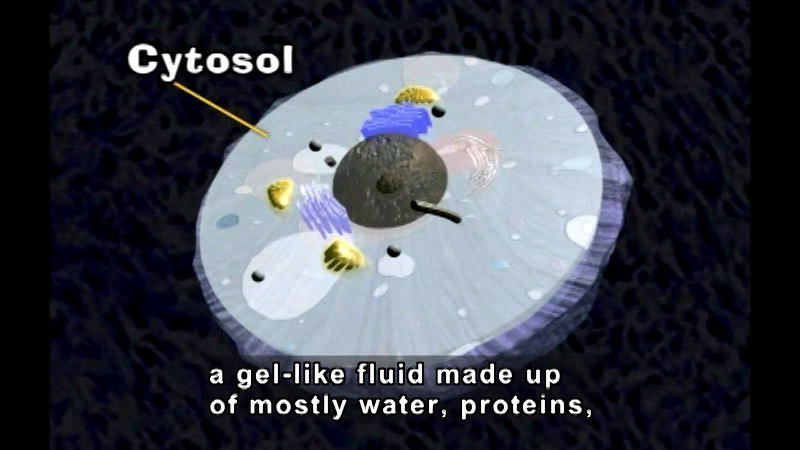
Deeply explores the structure of both plant and animal cells. Demonstrates the different types of cells, their components, and their functions
(Source: DCMP)
-
-
Single-Celled Organisms
-
 Video
Video

They're neither plants nor animals, yet they are some of the most important life-forms on Earth. This video segment explores the world of single-celled organisms: what they eat, how they move, what they have in common, and what distinguishes them from one another.
(Source: DCMP)
-
-
The Cell
-
 Video
Video
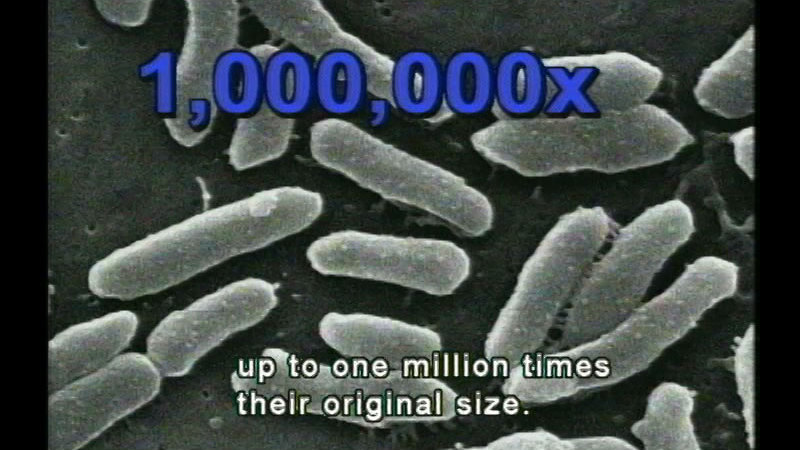
Provides an overview of the cell--the building block of life. Covers different kinds of microscopes, the discovery of cells, and the cell theory before focusing on a cell's characteristics and organization. Includes a quiz.
(Source: DCMP)
-
-
The Cell: Unit Of Life
-
 Video
Video
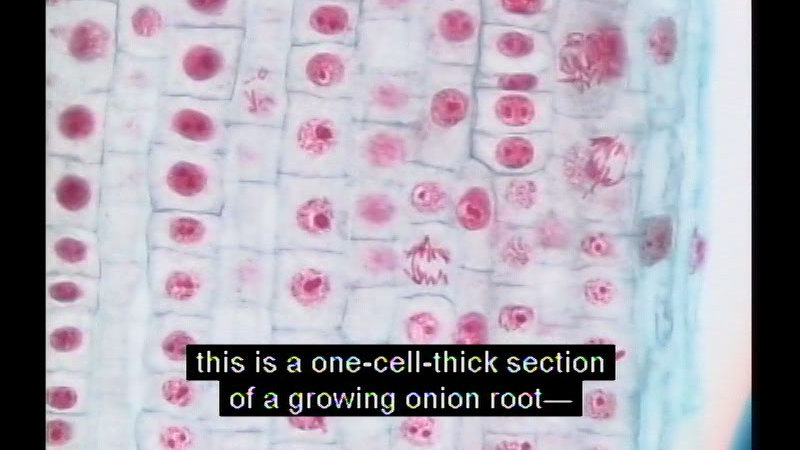
Part of the "Inside the Living Cell" series. Provides an overview of the different kinds of cells, emphasizing the fact that all cells have a common organizational structure and carry out similar biochemical processes. Presents the discovery of cells, cell structures, organelle function, cell varieties, and the chemistry of life.
(Source: DCMP)
-
-

A taxonomist explains the current classification system for all living things. Beginning with Aristotle's two kingdom division, today there are five kingdoms, with talk of changing to six. Uses the product groupings in a grocery store to clarify the concept. Looks at the differences of each kingdom: Monera, Protista, Fungi, Plantae, and Animalia. Stresses that the more we learn, the more likely this system will change yet again.
(Source: DCMP)
-
The Eye
-
 Video
Video
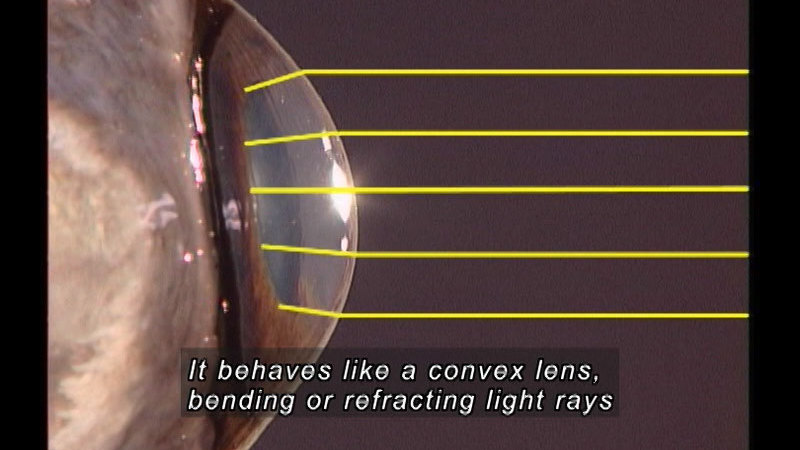
The eye is one of each human's major sense organs. It gathers light information and transforms it into a signal that is used by the brain to formulate an appropriate response. How does this process work? What are the structures involved, and what do they do? These questions are answered using a unique, integrated approach that combines the anatomy and function of the eye. Includes detailed footage of the dissection of the bovine eye.
(Source: DCMP)
-
-
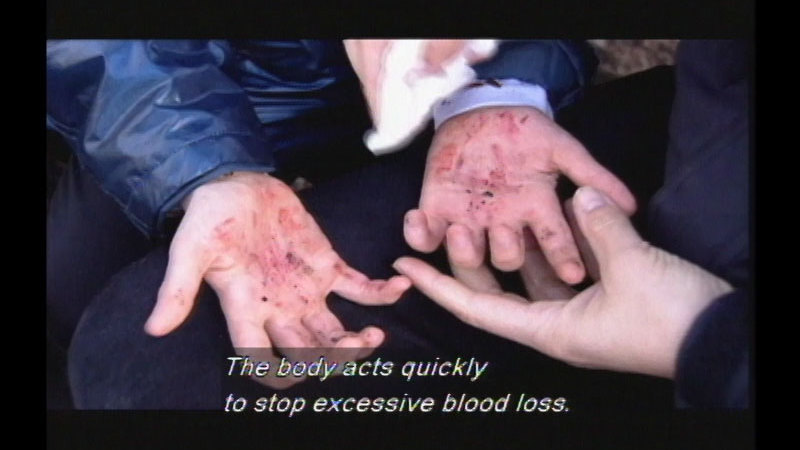
The immune system has a tough job keeping human bodies free of harmful microbes. Humans come in contact with germs and bacteria every day, and the immune system is challenged to protect the body. Explores how the human body goes to battle against germs in order to keep people healthy and how sometimes the immune system requires assistance.
(Source: DCMP)
-

The Magic School Bus is an award winning animated children’s television series based on the book series of the same title by Joanna Cole and Bruce Degen. It is notable for its use of celebrity talent and being both highly entertaining and educational. It's the night of the rock lovers' annual Granite Awards, and Arnold is about to become the first kid ever to win the coveted Rocky Award. He's so excited; all he's been able to eat for weeks are "Seaweedies.” When he arrives for the big event, he’s nervous and orange. Once the class determines that the orange isn't on Arnold's skin, they shrink down to explore what's underneath. They discover that his whole body is made of living cells, and they're all orange.
(Source: DCMP)
-
To what degree are we genetically programmed with certain traits and abilities? Looks at recent technologies and scientific discoveries and considers the classic "nature versus nurture" discussion. Segments cover identical twins, the science of biotechnology, and the genetic inheritance of working dogs. Investigates the similarities in personality shared by identical twins. Explains how recent breakthroughs in genetics research and DNA have created new ways to solve crimes, breed (clone) animals, and extend human life. Discusses cross-species cloning, human cloning, and gene therapy. Shows how assistance and search-and-rescue dogs can be taught to overcome their inborn instincts and fear.
(Source: DCMP)
-
Viruses & Monerans
-
 Video
Video
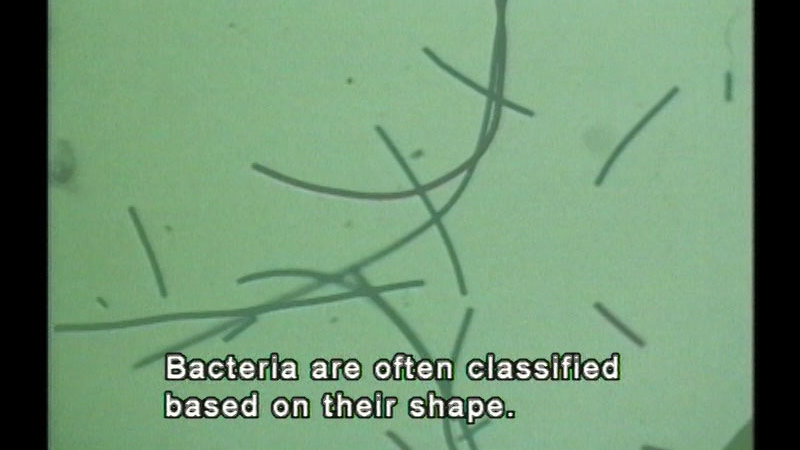
Outlines the characteristics, shapes, and structures of viruses and monerans, more commonly called bacteria. Notes ways that both affect our lives.
(Source: DCMP)
-
-
Your Body
-
 Video
Video
Special attention is given to the healthy maintenance of growing bodies. Concepts and terminology discussed include: body systems, cells, tissues, organs, health, and body needs.
(Source: DCMP)
-