Anatomy
Collection of anatomy resources
curated by Benetech
Resources 21
-

Investigates the major body systems that are important during physical activity: the skeletal, muscular, cardiovascular, respiratory, and nervous systems. Examines each of these systems, their parts, their functions, and how they work. Also, explores the contribution and interaction of the systems when we exercise and while we are rest.
(Source: DCMP)
-
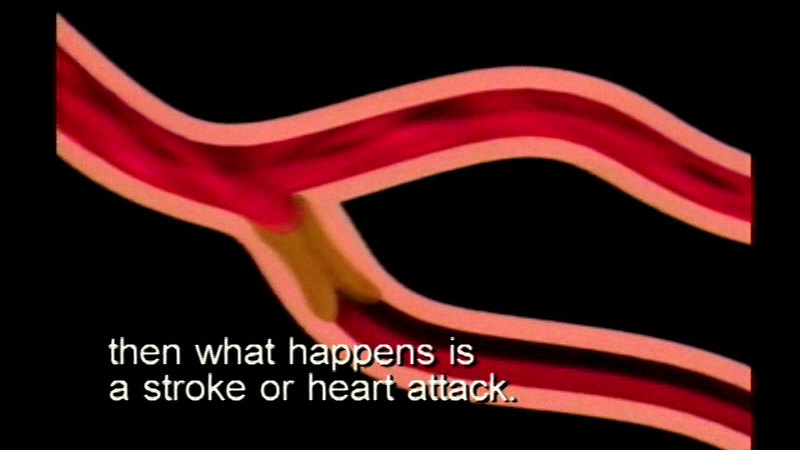
The heart is a pump, moving blood throughout the body via arteries and veins. Uses graphics to clarify the circulatory system and its functions. Notes the effects of exercise, nutrition, smoking, and infections on this system, and briefly illustrates coagulation, nosebleeds, and vaccinations.
(Source: DCMP)
-
Eyeball
-
 Image
Image
-
 PDF
PDF
-
 Text Document
Text Document
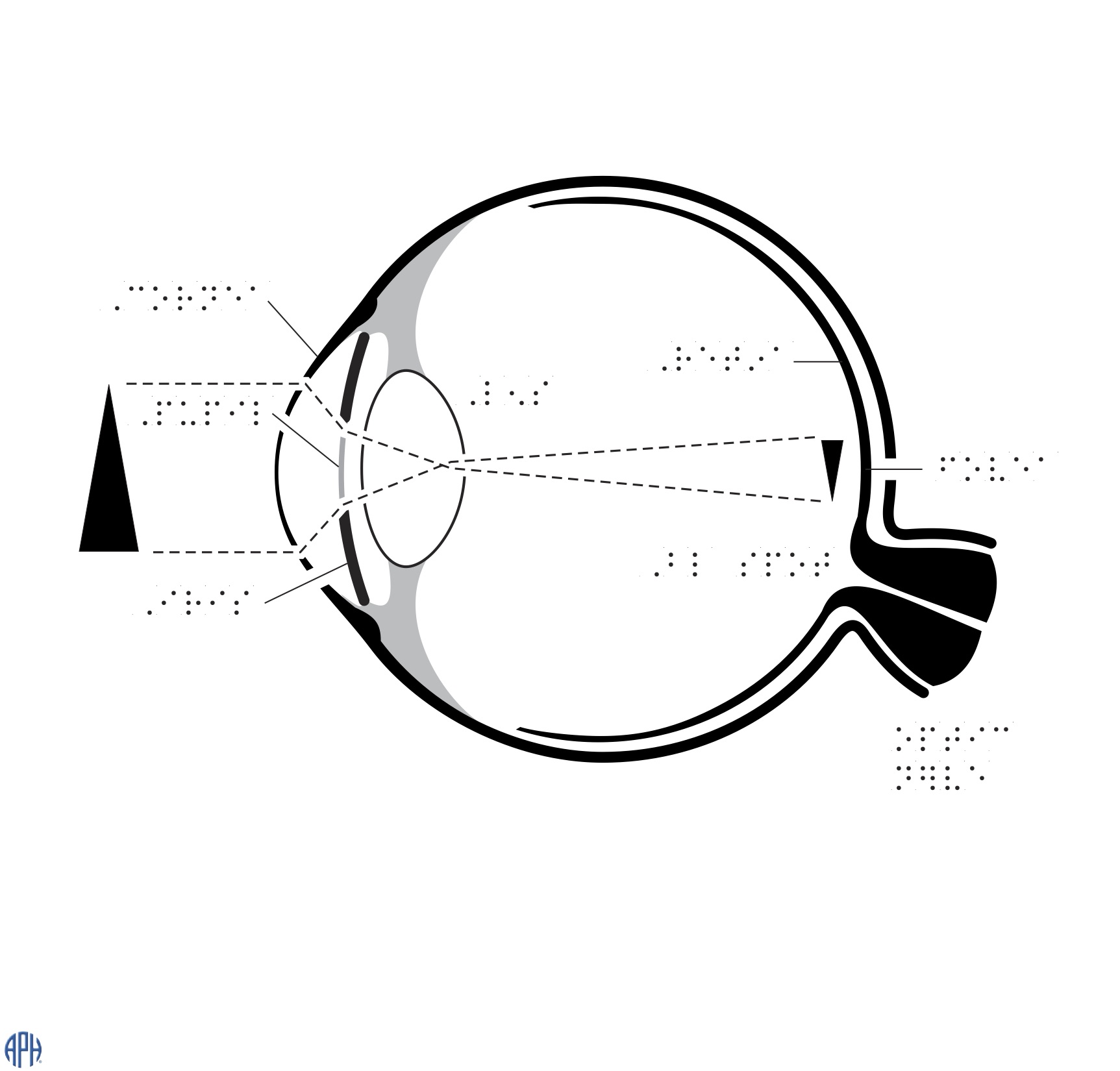
Braille labelled diagram showing the parts of an eye.
(Source: APH)
-
-

The human body needs to take in food and water found in the environment, and through a sequence of mechanical and chemical processes, it converts that food into nutrients that sustain all the body's activities. The digestive tract alone has nine major organs devoted to this process, and the renal tract has three. Join Dr. Mark Reisman as he provides you with a look at the anatomy and physiology of the many organs and structures of digestion. Lastly, explores the properties of metabolism and nutrition.
(Source: DCMP)
-
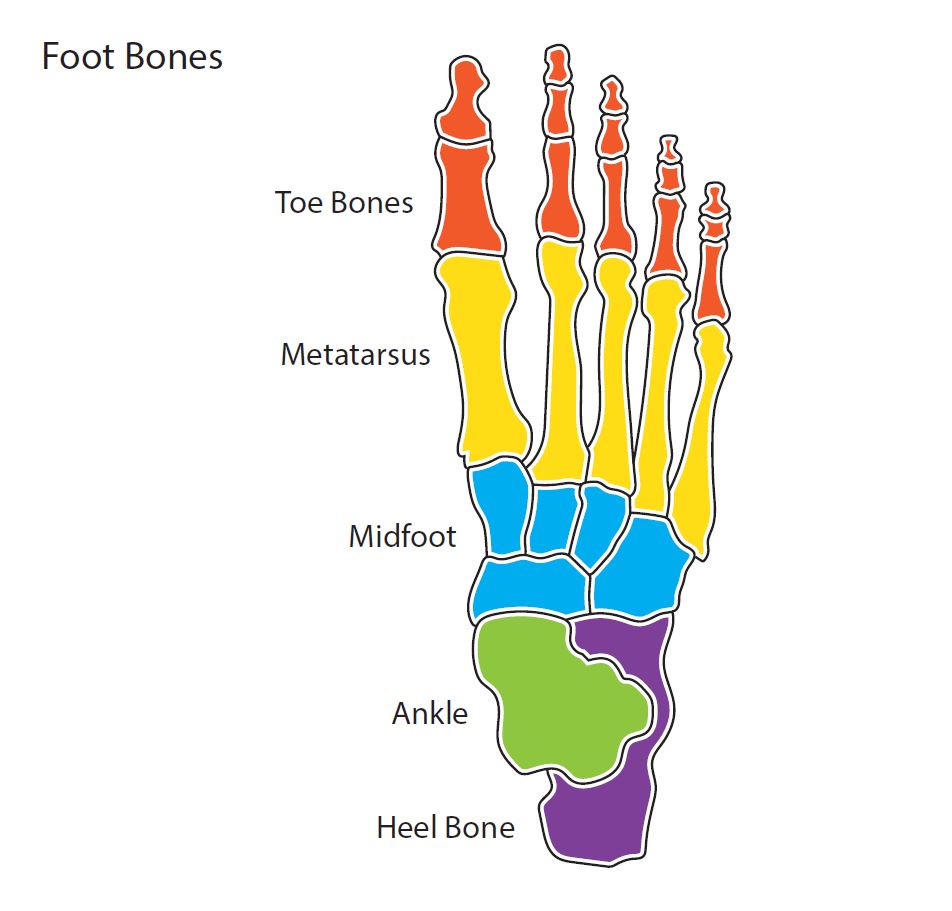
Foot Bone Diagram
-
 Image
Image
-
 Text Document
Text Document
-
 PDF
PDF
-
 2.5D Tactile Graphic
2.5D Tactile Graphic
Diagram showing the bones in a human foot. Design modalities for the image include braille with and without labels, print with and without labels in greyscale, color, and texture.
(Source: Benetech)
-
-
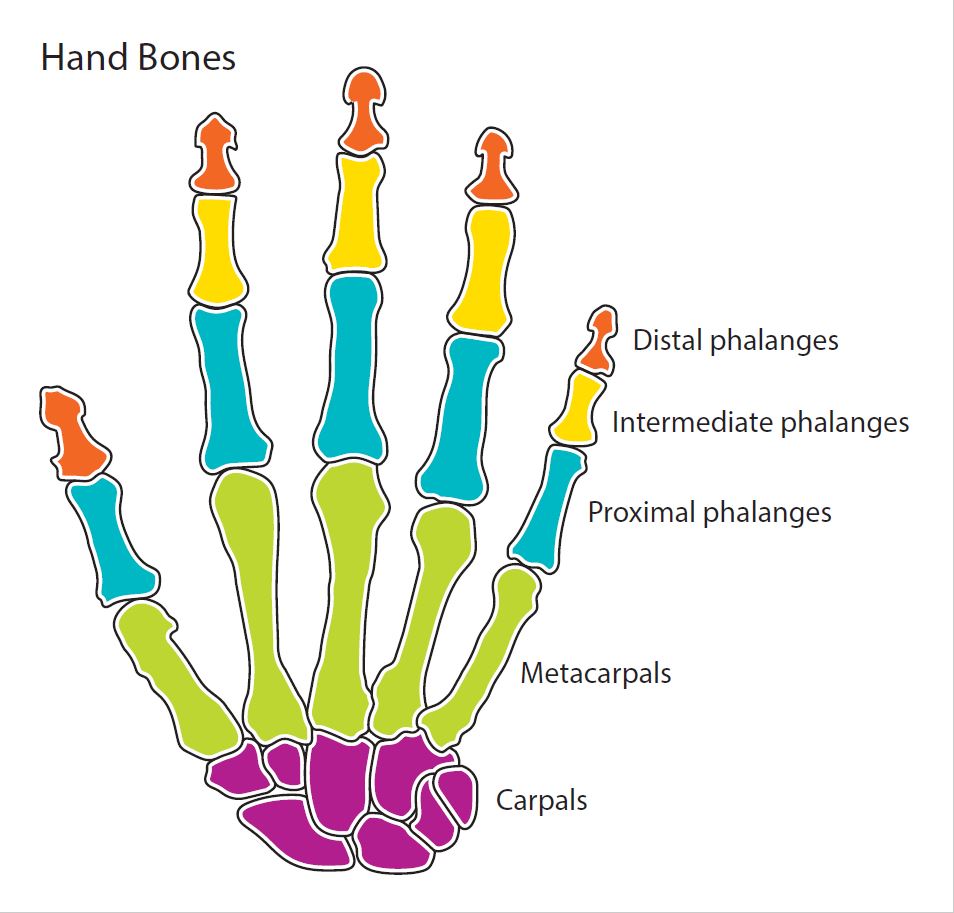
Hand Bone Diagram
-
 Image
Image
-
 Text Document
Text Document
-
 PDF
PDF
-
 2.5D Tactile Graphic
2.5D Tactile Graphic
Diagram showing the bones in a human hand. Design modalities for the image include braille with and without labels, print with and without labels in greyscale, color, and texture.
(Source: Benetech)
-
-
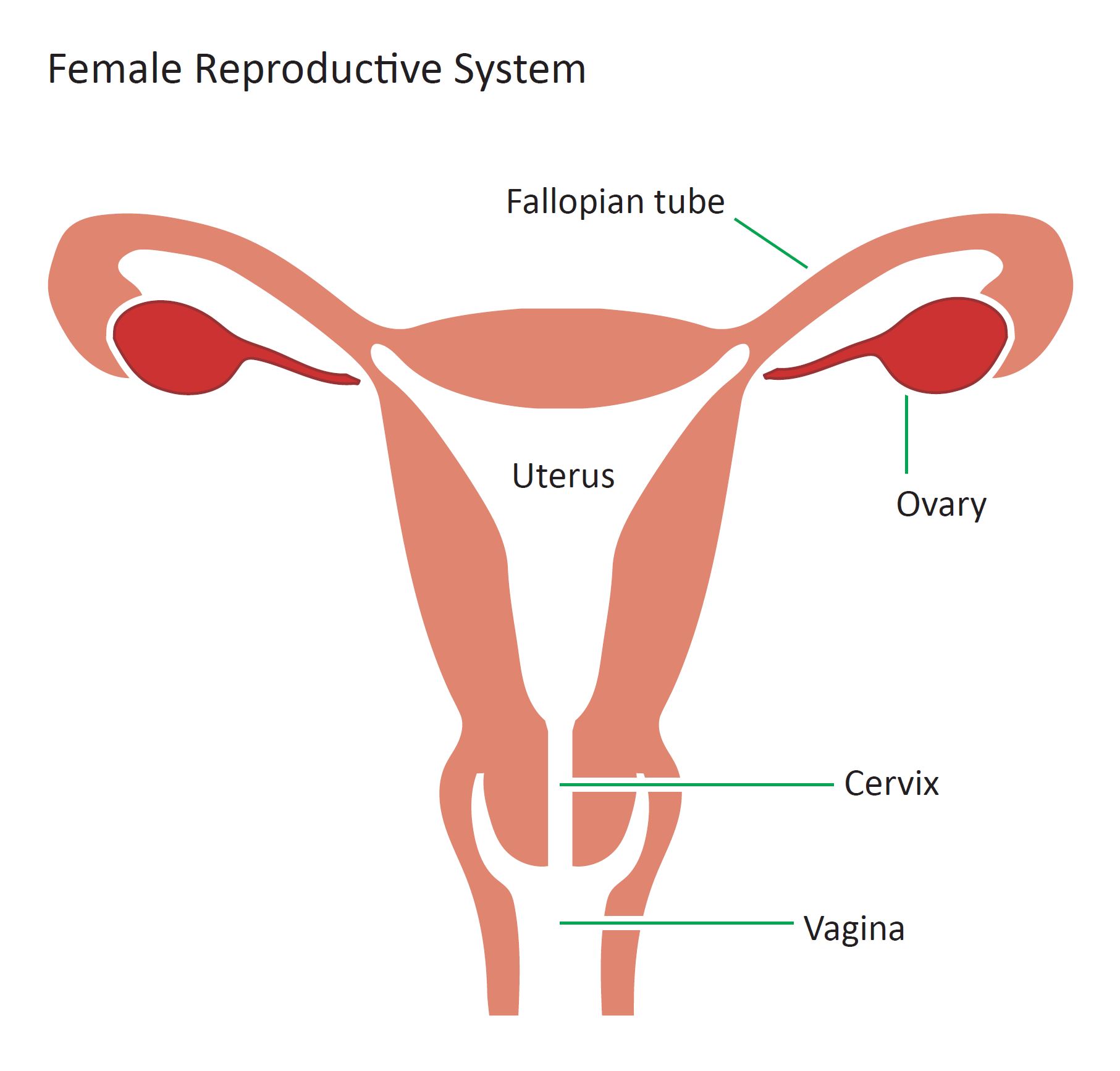
Female Reproductive System
-
 Image
Image
-
 Text Document
Text Document
-
 PDF
PDF
-
 2.5D Tactile Graphic
2.5D Tactile Graphic
Diagram of the internal view of the female reproductive system. Design modalities for the image include braille with and without labels, print with and without labels in greyscale, color, and texture.
(Source: Benetech)
-
-
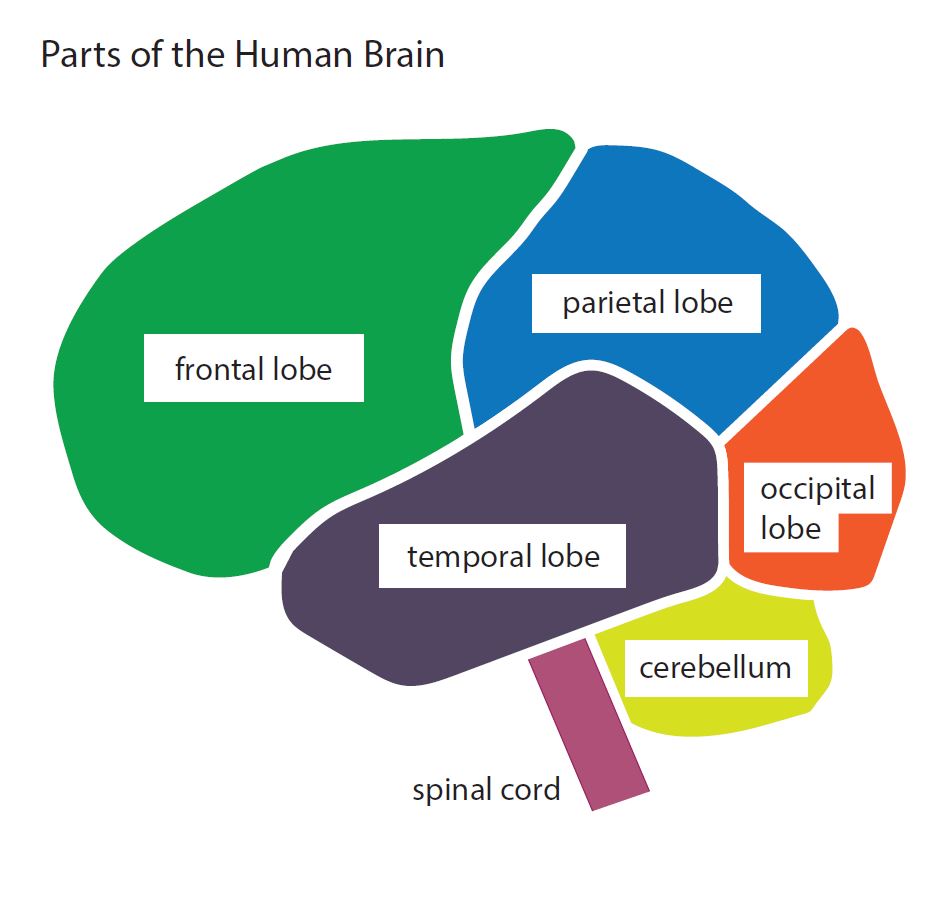
Basic Brain Diagram
-
 Image
Image
-
 Text Document
Text Document
-
 PDF
PDF
-
 2.5D Tactile Graphic
2.5D Tactile Graphic
Basic diagram of the parts of the human brain. Design modalities for the image include braille with and without labels, print with and without labels in greyscale, color, and texture.
(Source: Benetech)
-
-
Brain
-
 Image
Image
-
 Text Document
Text Document
-
 PDF
PDF
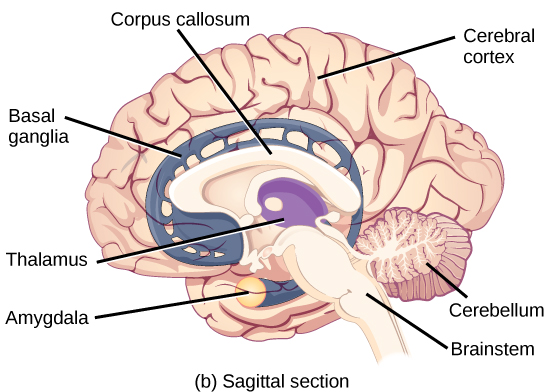
Sagittal, or side view of the human brain shows the different lobes of the cerebral cortex. The frontal lobe is at the front center of the brain. The parietal lobe is at the top back part of the brain. The occipital lobe is at the back of the brain, and the temporal lobe is at the bottom center of the brain. The motor cortex is the back of the frontal lobe, and the olfactory bulb is the bottom part. The somatosensory cortex is the front part of the parietal lobe. The brainstem is beneath the temporal lobe, and the cerebellum is beneath the occipital lobe.
(Source: OpenStax)
-
-
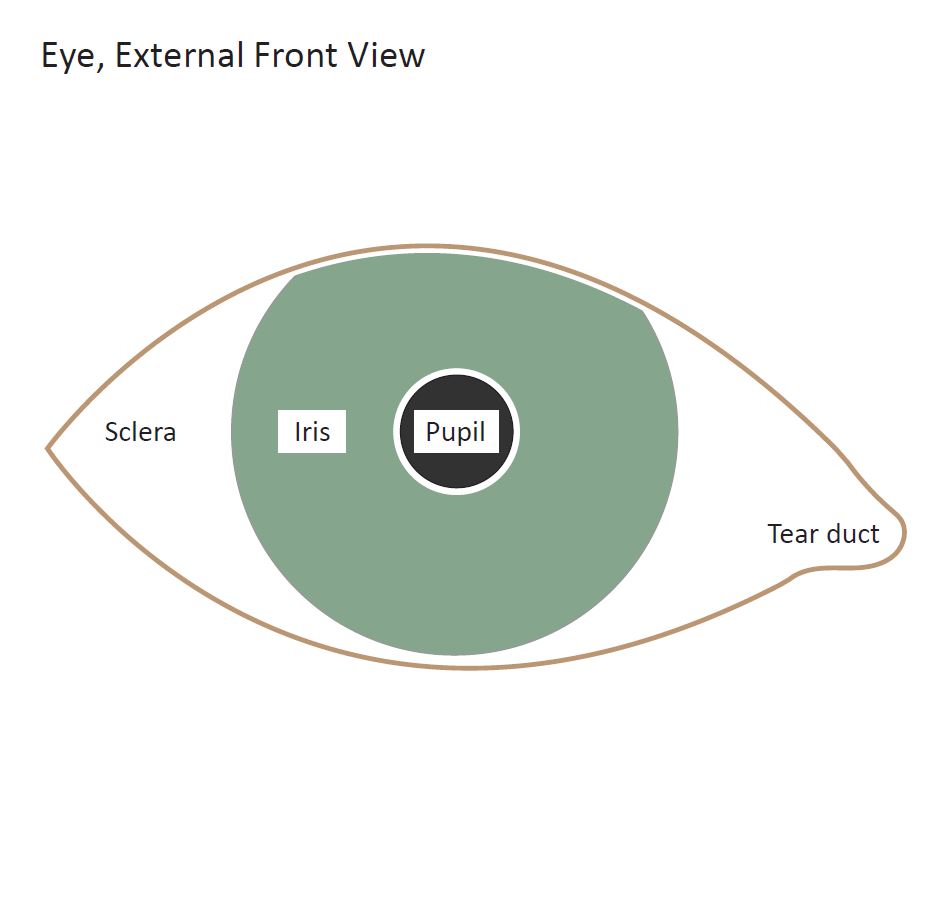
Eye, External Front View
-
 Image
Image
-
 Text Document
Text Document
-
 PDF
PDF
-
 2.5D Tactile Graphic
2.5D Tactile Graphic
Diagram of the external view of a human eye. Design modalities for the image include braille with and without labels, print with and without labels in greyscale, color, and texture.
(Source: Benetech)
-
-
Frog Dissection (with tactile 2.5D images)
-
 2.5D Tactile Graphic
2.5D Tactile Graphic
-
 Image
Image
-
 PDF
PDF
-
 Text Document
Text Document
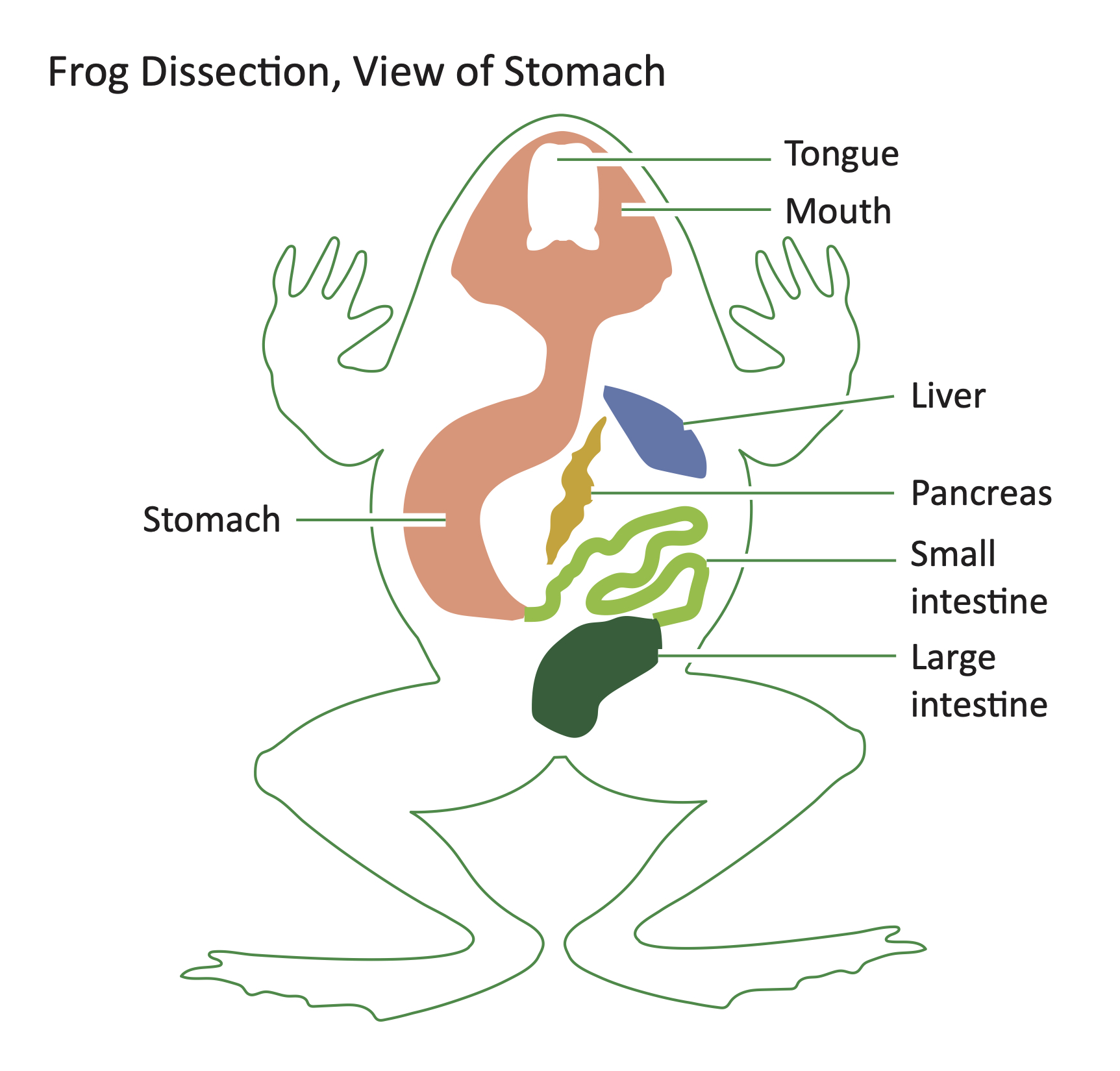
Diagram of the internal organs of a frog as shown in a dissection. Design modalities for the image include braille with and without labels, print with and without labels in greyscale, color, and texture.
(Source: Benetech)
-
-
Inner Ear
-
 Image
Image
-
 Text Document
Text Document
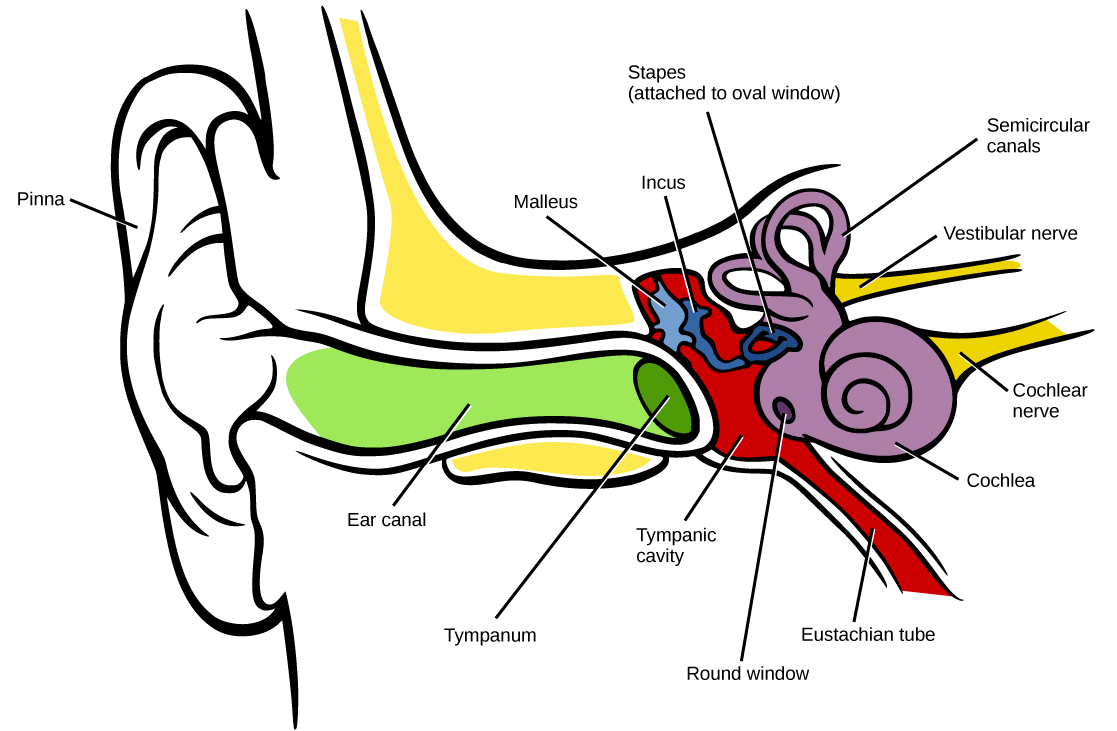
Labelled parts of the Human Inner Ear
(Source: OpenStax)
-
-
Kidney and Bladder
-
 Image
Image
-
 Text Document
Text Document
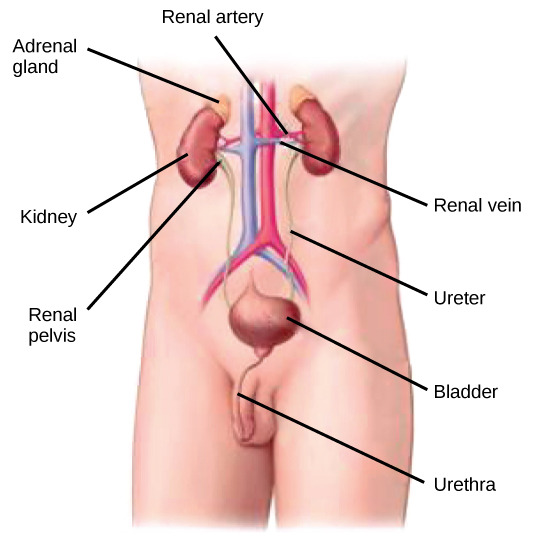
Labelled parts of the Human Bladder and Kidneys
(Source: OpenStax)
-
-
Large Intestine
-
 Image
Image
-
 Text Document
Text Document
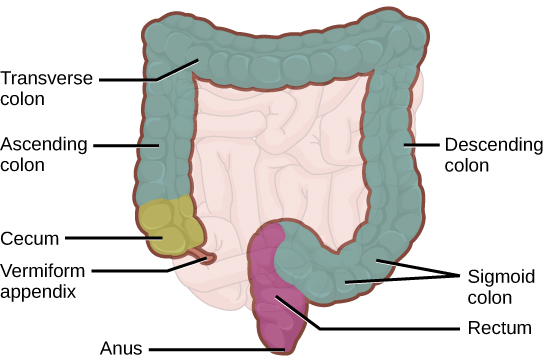
Labelled parts of the Human Large Intestine
(Source: OpenStax)
-
-
Touch, taste, smell, hearing, and sight: the human body's five major senses. They are senses that have evolved independently over millions of years but are brought together by our marvelous central nervous system into the most refined way of interacting with the environment of any species on the planet. Join Dr. Mark Reisman as he provides you with a look at the anatomy and physiology of each of these sensory systems and shows how the brain uses them to produce what we call being human.
(Source: DCMP)
-
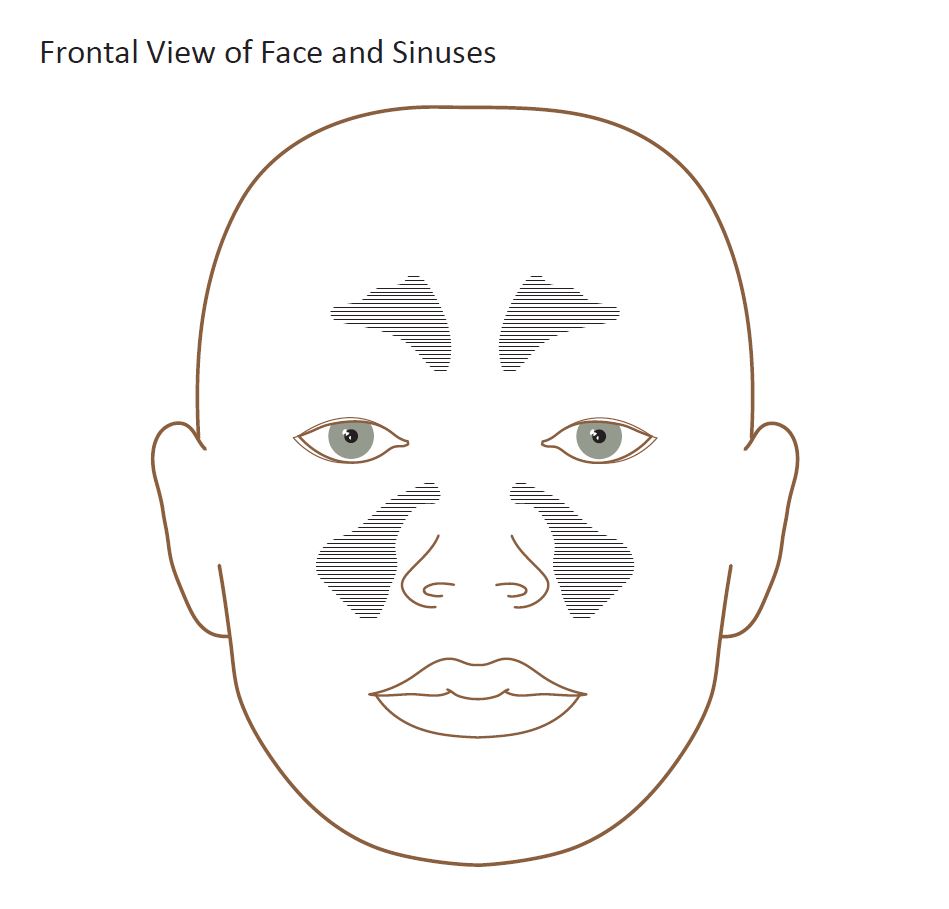
Nose and Sinus Diagram
-
 Image
Image
-
 Text Document
Text Document
-
 PDF
PDF
-
 2.5D Tactile Graphic
2.5D Tactile Graphic
Diagram of the human nose and sinus. Design modalities for the image include braille with and without labels, print with and without labels in greyscale, color, and texture.
(Source: Benetech)
-
-

The endocrine system maintains the body's delicate chemical balance. Describes the location, function, and effects of the major endocrine glands, and notes their close relationship to the nervous system. Some discussion of diabetes and hormonal imbalances.
(Source: DCMP)
-
The Eye
-
 Video
Video
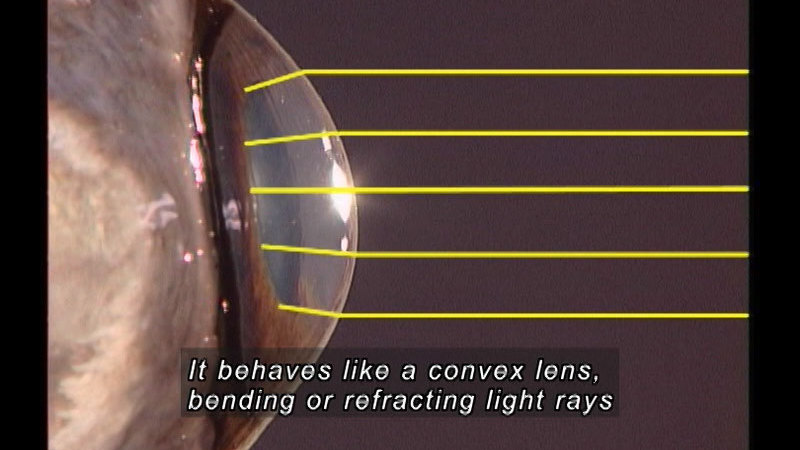
The eye is one of each human's major sense organs. It gathers light information and transforms it into a signal that is used by the brain to formulate an appropriate response. How does this process work? What are the structures involved, and what do they do? These questions are answered using a unique, integrated approach that combines the anatomy and function of the eye. Includes detailed footage of the dissection of the bovine eye.
(Source: DCMP)
-
-

The Magic School Bus is an award winning animated children’s television series based on the book series of the same title by Joanna Cole and Bruce Degen. It is notable for its use of celebrity talent and being both highly entertaining and educational. Ms. Frizzle takes the class with her when she brings the Magic School Bus to the body shop for repairs. While there, Ralphie wants to use extra parts at the shop to make a robot. Ms. Frizzle then teaches the class how bones, muscles and joints all work together to help us move.
(Source: DCMP)
-
Tongue
-
 Image
Image
-
 Text Document
Text Document
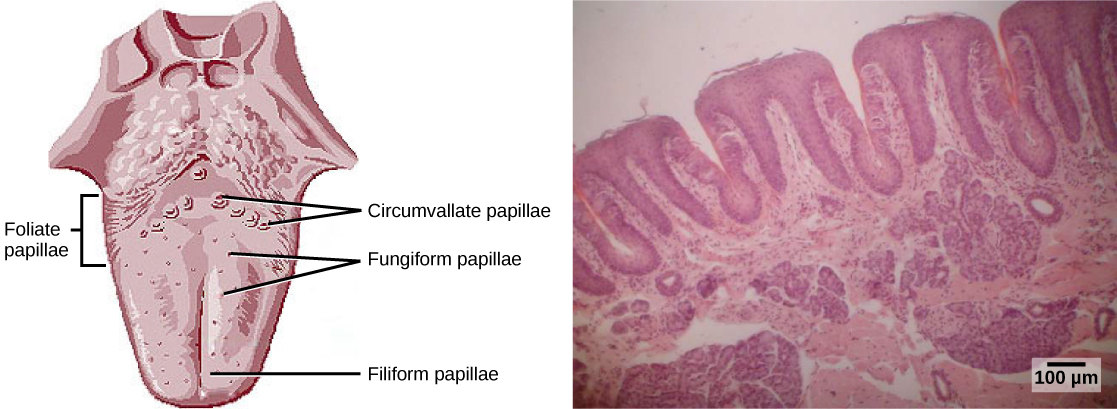
Tongue taste areas The tongue is a muscular organ in the mouth of most vertebrates that manipulates food for mastication, and is used in the act of swallowing. It is of importance in the digestive system and is the primary organ of taste in the gustatory system. The tongue's upper surface (dorsum) is covered in taste buds housed in numerous lingual papillae. It is sensitive and kept moist by saliva, and is richly supplied with nerves and blood vessels. The tongue also serves as a natural means of cleaning the teeth. A major function of the tongue is the enabling of speech in humans and vocalization in other animals. The human tongue is divided into two parts, an oral part at the front and a pharyngeal part at the back. The left and right sides are also separated along most of its length by a vertical section of fibrous tissue (the lingual septum) that results in a groove, the median sulcus on the tongue's surface. There are two groups of muscles of the tongue. The four intrinsic muscles alter the shape of the tongue and are not attached to bone. The four paired extrinsic muscles change the position of the tongue and are anchored to bone. Do you have good taste? In this video segment, Dr. Linda Bartoshuk explores the sense of taste in humans - why we have it, and what happens when we lose it. Learn why the sense of smell is also important to our experience of food. Footage from NOVA: "Mystery of the Senses: Taste".
(Source: OpenStax)
-
-
Veins and Arteries
-
 Image
Image
-
 Text Document
Text Document
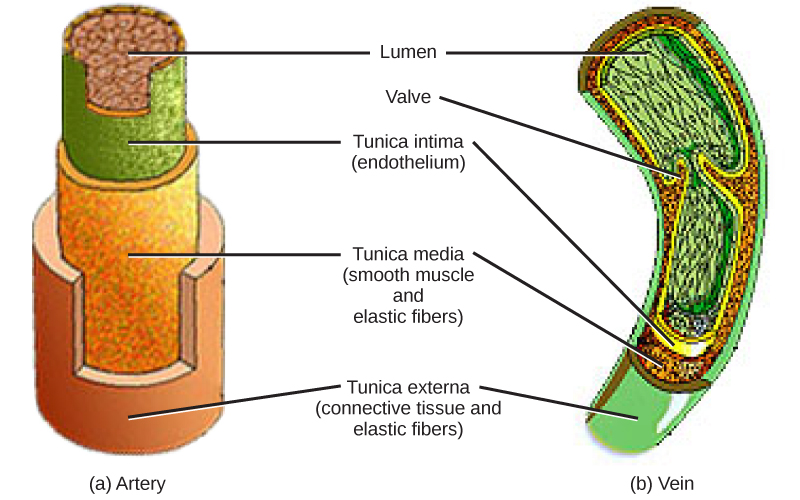
Cross sectional view of vein vs an arterie
(Source: OpenStax)
-